Expert Surgical Care, Compassionate Healing a
November 29, 2024
Expert Surgical Care, Compassionate Healing c
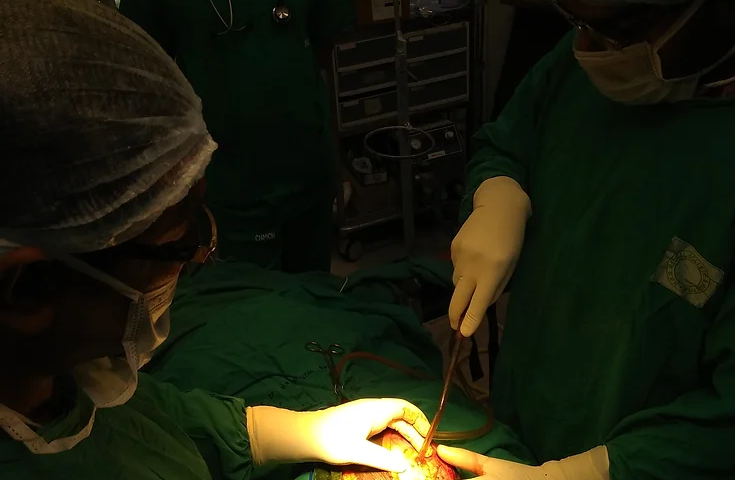
November 29, 2024Hernia in general defined as the abdominal exit of a part of bowel or an organ through the wall of the cavity in which it normally resides. A Western estimate reveals that the lifetime risk of developing a hernia is about 2%. So hernia repairs is one of the most frequent general surgery operations.
.

The most frequent hernia type is inguinal. According to some classical reference books, the frequency of abdominal wall hernias is as follows: inguinal (70%–75%), femoral (6%–17%), and umbilical (3%–8.5%), followed by rare forms (1%–2%). Over recent years, there have been some changes not only in the frequencies but also in the repair preferences and anesthetic techniques in daily surgical practice.
Hernia repair surgery or herniorrhaphy involves returning the displaced tissues to their proper position and repair the defect with suture. Hernioplasty is a type of hernia repair surgery where a mesh patch is sewn over the weakened region of tissue. Both hernia surgery techniques can either be done through a large incision or laparoscopically, which involves accessing the misplaced tissues through three or four small cuts made adjacent to the hernia. Until about 25 years ago, the only options to repair a hernia was an open tension repair. Certain patients will benefit from an open procedure, especially if there are multiple hernias that are not easily reachable with traditional laparoscopic devices. Other reasons for choosing an open procedure include severe obesity, dense scar issue in the area of the procedure and a propensity for excessive bleeding. In some cases, open surgery also reduces the possibility of the recurrence of the hernia. Patients with recurrent hernias may benefit from an open procedure.
As minimally invasive techniques and devices are enhanced, an ever-greater proportion of hernia surgeries are being performed laparoscopically. During the procedure, two tiny incisions are made in the area of the hernia and a larger incision is made within the umbilicus. A surgical mesh is placed over the hernia and affixed to the abdominal wall.
Minimally invasive surgery has many benefits in the form of less pain and blood loss as well as a shorter hospital stays after surgery. However, minimally invasive surgery may not be appropriate for all hernia patients, especially those suffering from multiple hernias that cannot be reached with laparoscopic tools, obese patients or those with significant scarring from previous procedures in the area.
There’s been a great deal of debate over whether surgical mesh should be used to repair a hernia. However, mesh remains the gold standard for hernia repair because it creates a stronger, longer-lasting solution that is less likely to allow for hernia recurrence when compared to a traditional tension or suture repair. Conventional laparoscopic surgeries of direct inguinal hernia include two methods, transabdominal preperitoneal hernioplasty (TAPP) and totally extraperitoneal hernioplasty(TEP). Both methods are performed using synthetic mesh without suturing the hernia defect and require extensive mesh coverage.Operation time and postoperative hospital stay showed no difference between two groups.
Certain factors can complicate hernia repair surgeries and increase the risk of negative side effects or the surgery failing. Common risk factors for hernias and undergoing hernia repair include: age, obesity, pregnancy, family history, occupation, constipation, smoking, high blood pressure, connective tissue disorders, malnutrition.